After growing from $5 trillion just a few years ago, the forex market is now by far the biggest and most liquid financial market in the entire world. Its estimated worldwide average daily turnover exceeds US$6.5 trillion.
One of the most important features of the forex market is that there is no singular central marketplace or exchange and that all trading occurs electronically over computer networks. This is an over-the-counter (OTC) transaction.
How do Forex markets work?
In opposition to trading in commodities or shares, forex trading occurs instantly between two parties in an over-the-counter (OTC) market. A worldwide network of banks that are dispersed among four significant forex trading hubs in various time zones—London, New York, Sydney, and Tokyo—control the forex market. There is no central hub, so you can swap currency whenever you like.
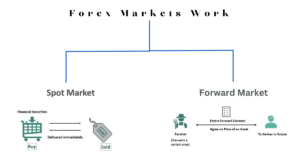
The currency market is divided into three categories:
Spot forex market: A currency pair is physically exchanged at the exact moment the transaction is finished, “on the spot,” or quickly.
Forward foreign exchange market : A contract is made to purchase or sell a specific amount of money at a specific price. A predetermined future date or a variety of future dates are used to settle the contract.
Futures forex market: A contract to buy or sell a certain amount of a certain money at a certain price and date in the future
The majority of forex traders forecast exchange rates in order to profit from changes in market prices rather than with the intention of acquiring real currency.
Read Here: Pi Network : Building the Future of Decentralized Finance
What Is a Base and Quote Currency?
The foundation currency and the quote currency make up a forex pair. Always mention the base currency first. The price of a forex exchange is the amount that one unit of the base currency is worth in the quotation currency. Forex trading is always described in pairs because it always entails selling one currency in order to purchase another.
A three-letter code that usually consists of two letters designating the area and one letter designating the currency is used to identify each of the two currencies in the pair. For instance, buying the British pound and selling the US dollar are both possible with the conversion rate GBP/USD.
In the example below, the stated currency is USD, and the base currency is GBP. If the GBP/USD conversion rate is 1.35361, then one pound is equivalent to 1.35361 dollars.
The price of the set will increase if the value of the pound relative to the dollar increases, making one pound worth more dollars. If so, the cost of the package will go down. Consequently, you can purchase the pair if you believe that the base currency in a combination will likely strengthen relative to the quoted currency (going long). You could trade it if you think the pair will decrease in value (going short).
Who Is in Charge of the Currency Market?
When learning about the forex market, many traders have one concern in mind: who regulates it?
It’s a smart query that novices frequently ask. The majority of the market is actually governed by four international networks, including institutions from London, Sydney, New York, and Tokyo.
These institutions are owned and managed by businesses. But there are other participants who are crucial in this scenario.
Forex Trading in India
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) oversee forex transactions in India (SEBI). Indian residents are allowed to trade forex through authorized dealers, banks, and brokers who are registered with the RBI and SEBI.
The RBI has placed certain restrictions on forex trading in India, such as limiting the amount of currency that can be traded and prohibiting trading in certain currency pairs. Additionally, forex trading by individuals is allowed only for the purpose of hedging their foreign exchange exposure for permissible transactions under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).

It is important for traders to ensure that they are dealing with authorized dealers, banks, and brokers who are registered with the RBI and SEBI, and to comply with all the regulations and guidelines issued by these regulatory bodies. If you don’t, there could be fines and civil repercussions.
Overall, forex trading can be a lucrative investment opportunity, but it is important to approach it with caution and follow all the applicable rules and regulations in India.
Read Here: BharOS: A User-Friendly Operating System
Conclusion
Forex, or foreign exchange, refers to international currency trading. It works through a global network of financial institutions, and its prices are influenced by various factors such as economic and political events.
Forex trading involves speculating on the changes in currency prices, and traders can make profits by buying low and selling high. It can be done through online trading platforms that provide access to the market and various tools and resources for analysis and decision-making.
However, forex trading also carries risks, and traders should be aware of the potential losses and have a clear understanding of the market and their strategies.
In conclusion, forex is a complex and dynamic market that can offer opportunities for profit, but it requires knowledge, skills, and discipline to succeed.
